You are here
New Releases
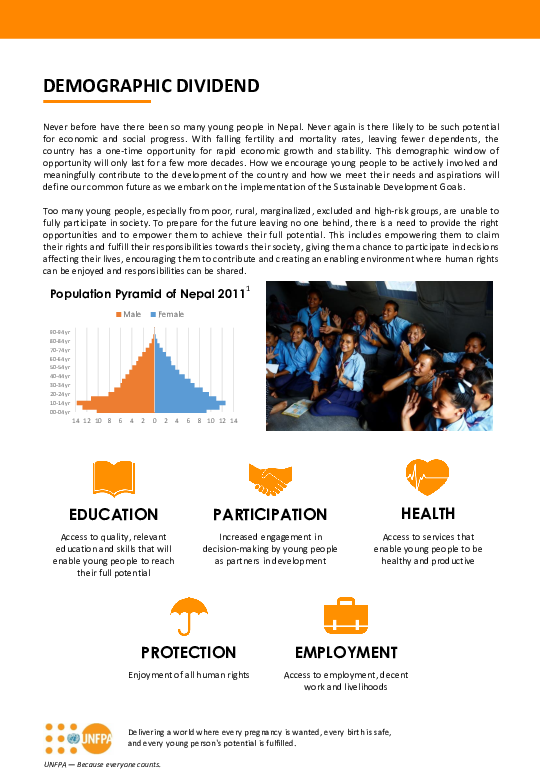
Fact Sheet: Demographic Dividend in Nepal
This fact sheet was prepared by UNFPA Nepal for the purpose of informing parliamentarians, policymakers, political parties, civil society leaders, development partners, women, young people and the general public.
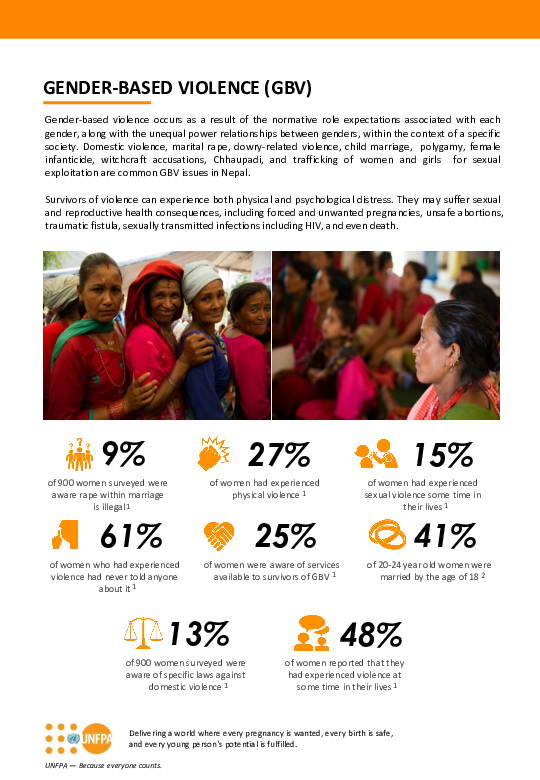
Fact Sheet: Gender-based Violence in Nepal
This fact sheet was prepared by UNFPA Nepal for the purpose of informing parliamentarians, policymakers, political parties, civil society leaders, development partners, women, young people and the general public.
UNFPA Nepal Brochure
Established in 1971 in Nepal, UNFPA has been working with the Government of Nepal, development partners, parliamentarians, civil society, young people and other stakeholders to promote sexual and reproductive health and rights for all, ensure that no woman dies giving life and enable marginalized, poor and hard-to-reach people to live in dignity and enjoy their human rights.
UNFPA works both at national and at local level through five-year programme cycles under the framework of the UN Development Assistance Framework. Our priorities are aligned with the country's priorities as spelled out by the Government of Nepal in three key interrelated areas: reproductive health, gender equality and reproductive rights and population dynamics.
सन् १९७१ देखि नेपालमा कार्य गर्न थालेयता संयुक्त राष्ट्रसंघीय जनसंख्या कोष (यूएनएफपीए) ले नेपाल सरकार, विकास साझेदारहरू, सांसदहरू, नागरिक समाज, युवा र अन्य सरोकारवालाहरूसित मिलेर सबैका लागि यौन तथा प्रजनन् स्वास्थ र अधिकार प्रर्वद्धन गर्न, बच्चा जन्माउने क्रममा कुनै महिलाको मृत्यु नहुने सुनिश्चित गर्न, सीमान्तिकृतहरूलाई सशक्त बनाउन, विपन्न र पहुँचदेखि टाढाका जनतालाई आत्मसम्मानका साथ जिउन र उनीहरूको मानव अधिकार उपयोग गर्नका लागि काम गरीरहेको छ । संयुक्त राष्ट्रसंघको विकास सहायता फ्रेमर्वक भित्र रहेर यूएनएफपीएले पाँच वर्षे कार्यक्रमको चक्रहरूमार्फ्त राष्ट्रिय र स्थानीय दुबै तहहरूमा काम गर्दछ । हाम्रा प्राथमिकताहरू नेपाल सरकारले तोकेका नेपालका प्राथमिकताहरूसित मिल्दाजुल्दा छन् जुन तीन प्रमुख अन्तर्सम्वन्धित क्षेत्रहरू– यौन तथा प्रजनन् स्वास्थ्य र अधिकारहरू, लैंगिक समानता र जनसंख्याको गतिशीलतासँग सम्वद्ध छन् ।
SDGs Booklets in Nepali and English
The Sustainable Development Goals aim to end poverty by 2030. World leaders have set a plan of action for people, planet and prosperity. Eradicating poverty in all its forms and dimensions, including extreme poverty, is the greatest global challenge and an indispensable requirement for sustainable development. The 17 SDGs build on the Millennium Development Goals and complete what they did not achieve. They seek to realize the human rights of all and to achieve gender equality and the empowerment of all women and girls. They are integrated and indivisible and balance the three dimensions of sustainable development: the economic, social and environmental.
UN System in Nepal has published two easy-to-read SDG booklets in both Nepali and English and they are now available for download.
Ending Impunity for Child Marriage in Nepal
Child marriage affects both boys and the girls, however, it disproportionately affects girls’ ability to enjoy their rights and freedoms, especially due to the serious risks of sexual and reproductive harms associated with this practice. Child marriage triggers a continuum of reproductive and sexual harms and violations by exposing girls to forced initiation into sex and unprotected sex, as well as early, unplanned, and frequent pregnancies. Women and girls subject to child marriage are likely to face slavery-like practices such as servile marriage, sexual slavery, child servitude, child trafficking, and forced labor.19 According to the Nepal Demographic Health Survey (NDHS), 47% of women who first had sex before age 15 and 29% of women who first had sex between ages 15-19 have stated that their initial experience was forced and against their will, and a majority of these cases occurred within marriage.
The purpose of "Ending Impunity for Child Marriage in Nepal: A Review of Normative and Implementation Gaps" is to identify and inform policymakers, law enforcement officials, and human rights defenders, of the key legal gaps and inconsistencies that have undermined efforts to address child marriage in Nepal, particularly in light of the constitutional guarantees, national laws, and international human rights standards. This assessment highlights multiple challenges faced in the implementation of the existing affirmative laws and makes linkages to other causes of systemic discrimination in law and practice that contribute to impunity. It puts forward a set of concrete recommendations for addressing the gaps and challenges in order to promote access to justice for the victims of child marriage.
The policy brief was jointly produced by UNFPA, Justice and Rights Institute and Centre for Reproductive Rights.
Localizing Investments for the Demographic Dividend in Nepal
The demographic dividend is the accelerated development that can arise when a population has a relatively large proportion of working-age people coupled with effective human capital investment. In this poster, we measure human capital needs in Nepal at national and sub-national level using a “demographic dividend index” (DDI). We also map dependency ratios and human capital indicators in empowerment, education and employment for all districts in Nepal and identify priority areas for investments to enhance prospects for a demographic dividend.
Review of Curricula in the Context of Comprehensive Sexuality Education in Nepal
Nepal is a signatory of the International Conference on Population and Development (ICPD) and has been an active supporter of it. Nepal has endorsed the ICPD beyond 2014 review document, where the need for Comprehensive Sexuality Education (CSE) is highlighted. Nepal is one of the countries in South Asia, where CSE has been introduced formally in the school curriculum training in a meaningful way. In 2014, the Ministry of Education and UNFPA commissioned a study to review the status of CSE in Nepal against the six standards set out in the ITGSE UNESCO 2009.
Adolescent Girls in Disaster & Conflict
Safe spaces, mobile medical teams and youth engagement are effective ways to reach displaced, uprooted, crisis-affected girls at a critical time in their young lives. This publication is a collection of UNFPA-supported humanitarian interventions for reaching adolescents when crisis heightens vulnerability to gender-based violence, unwanted pregnancy, HIV infection, early and forced marriage and other risks. Together with other countries, it has a Nepal section (32-40 pages), showing how adolescent sexual and reproductive health was promoted after the devastating earthquake struck the country on April 25, 2016 through adolescent-friendly information corners.
District Disaster Preparedness and Response Plan, Kapilvastu
This District Disaster Preparedness and Response Plan for 2016 (कपिलवस्तु जिल्लाको विपद् पूर्वतयारी तथा प्रतिकार्य योजना २०७३) is an updated vulnerability assessment of Kapilvastu district that incorporates components of Minimum Initial Service Package (MISP) for reproductive health in emergencies. This plan (in Nepali) has been prepared by District Disaster Relief Committee (DDRC), Dang, with technical support of UNFPA, the United Nations Population Fund.
A Summary of Nepal Earthquake 2015: A Socio-Demographic Impact Study
The 2015 earthquake in Nepal and the subsequent aftershocks resulted in losses not only in terms of lives and physical infrastructures but also of historical, social, cultural and economic aspects of the country and its population. Thirty-one out of the 75 districts were affected by this devastation with 14 of them located in the Central and Western mountains and hills including Kathmandu Valley and categorized by the Government of Nepal as the most affected1. An estimated 5.4 million people live in these 14 districts.
In order to carry out a Damage and Loss Assessment, the government conducted a Post-Disaster Needs Assessment (PDNA) in May-June 2015 under the broader concept of building back better. While the PDNA assessed the damages of houses and buildings as well as the post-earthquake needs using a globally accepted methodology, it did not really focus on the socio-demographic impacts of the earthquake, that is, how households and communities had been affected, the level of local resilient social capacity to respond and how recovery and reconstruction efforts could be made more responsive.
Against this backdrop, it was decided to carry out this study in order to assess the socio-demographic impacts of the 2015 earthquake, with a focus on cultural diversity pertaining to household settings including caste/ethnicity, population dynamics (fertility, mortality, migration), as well as population size, composition and distribution. The study was meant to contribute to more cost-effective government policies on population dynamics resulting from the post-disaster context.
This survey was conducted among affected households in the 14 districts using multiple approaches and both quantitative and qualitative techniques to measure the socio-demographic impacts of the earthquake. CDPS/Tribhuvan University led the overall research and study design, fieldwork training, survey tool refinements, sample design, and data collection and management with the support from Ministry of Population and Environment, UNFPA, and IOM. The fieldwork was carried out during 20 November – 15 December 2015 with a total of 3,000 households surveyed, which was a statistically representative number.